CureFAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Answers to commonly asked arterial and metabolic disease questions.
Categories
Click on one of the categories below or type a keyword into the search bar to get started.
Recent FAQs
What tests are done at the CureCenter to measure arterial disease and its root causes?
There is a scientific understanding of the arterial disease (which causes heart attack, stroke and dementia) that is not offered by mainstream medical care. New testing methods and technology enable the CureCenter to offer more individualized and effective treatments…
The true inflammation nature of arterial disease (which causes heart attack, stroke and dementia) is not the basis of mainstream medical care. New testing methods and technology enable the CureCenter to offer more individualized and effective treatments.
Tests we perform and recommend not generally available from standard care include (but are not limited to):
Carotid Intima Media Thickness (CIMT) Testing: CIMT measures arterial wall thickness and documents atherosclerotic plaque stage and thickness. A thicker artery wall is an inflamed, older and sicker artery wall. This indicator of arterial inflammation predicts formation of atherosclerotic plaque and related events such as heart attack and stroke.
Arterial wall thickness (inflammation) is more relevant than luminal flow “blockage” in predicting new and unstable plaque formation. Unstable plaque rupture is the event we experience as a heart attack or stroke. This is more likely with new homogeneous unstable plaque. It becomes less likely as plaque becomes more homogeneous/healing and is minimal when plaque is calcified/healed/stable. Proactive optimal care can heal arterial disease and make your arteries healthier and younger with less risk of disability, death or need for rescue procedures.
Screening carotid ultrasound (CureScreen): This limited lower cost carotid ultrasound using point of care Butterfly iQ probe and system) is like a screening pap smear, mammogram or PSA to detect early cancer. If we find no disease, peace of mind is the benefit. If, however, even a little bit of arterial disease is found (like a little bit of cancer) the images can be sent for a CIMT report (see above) and then followed to make sure you are safer by following your CurePlan.
LpPLA2 (PLAC) Test: This enzyme rises when plaque and artery walls are inflamed or “hot.” You want your arteries to be “cool.” LpPLA2 drops with a less inflammatory diet, exercise, reduced insulin resistance, supplements (niacin, and bergamot and statins. It is a fire alarm or “meat thermometer.”
Myeloperoxidase (MPO): A rise in MPO should trigger a search for neutrophil involved inflammation, especially from the mouth. MPO indicates inflammation and erosion of the inner lining of the artery known as endothelium. A sudden rise should trigger a search for the inflammation that can cause arterial inflammation, leading to heart attack or stroke. Think of a caustic chemical spill inside your arteries. Like a skin abrasion, blood clots form and can occlude flow.
Microalbumin/Creatinine Ratio (MACR): MACR rises most commonly when blood pressure and blood glucose are poorly controlled. This causes dysfunction of the arterial wall endothelium, allowing albumin to leak into the urine in greater amounts. A leaky endothelium fails to protect the intima from processes that lead to inflammation. Think of it as another fire alarm.
For more information about these and other tests, go to
and other information from Cleveland Heart Lab, a major source of our testing
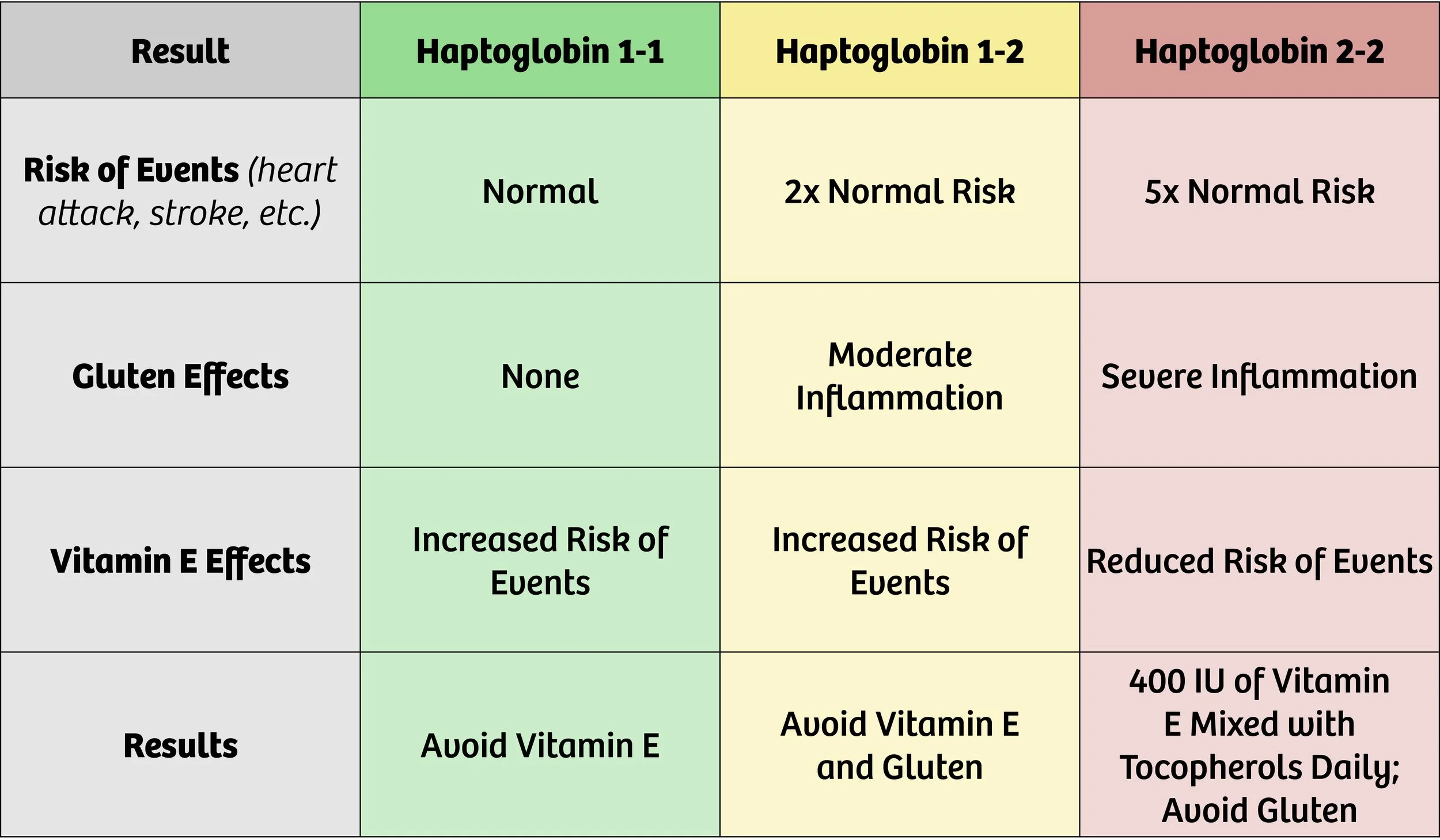
Haptoglobin Genotype: Your Haptoglobin genotype determines if Vitamin E offers protection or increases risk of arterial disease. In addition, individuals with the Hp 2-2 genome are more sensitive to gluten, forming an inflammatory mediator called zonulin that makes your gut “leaky” and raises the risk of autoimmune disease.
Insulin Resistance Testing: Optimally measured through an oral glucose tolerance test, insulin resistance (prediabetes) testing is important in identifying individuals who could be developing vascular complications before a Type 2 Diabetes diagnosis. The glucose tolerance test can identify insulin resistance long before the glucose starts to rise.
However, if there is other evidence of insulin resistance that does not require a visit to the lab, we can skip this step. Clues are seen in levels of nonoptimal HbA1c, glucose, triglycerides above 100, low HDL, and presence of small dense LDL (Pattern B).
The earliest detection for insulin resistance can be measured through body composition testing. At the CureCenter, we use the InBody 570, a device that can monitor insulin resistance response to changes in diet. Reducing insulin resistance is generally healthy for everyone, regardless of risk.
Homocysteine: Elevation increases risk of:
Osteoporosis - bone thinning
Thrombosis (blood clotting)
Heart Attack
Stroke
Dementia
Kidney failure
Neuropathy
Treatment is supplementation with methylated folic acid. Dietary sources of folic acid are leafy greens like spinach and kale.
This paper from the American Heart Association offers a good summary of Homocysteine.
Coronary Artery Calcium Score (CACS): This CT scan detects mature calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. However, it can miss new noncalcified plaque. This test is not useful in monitoring therapy progress/benefit. We recommend CACS when CIMT does not reveal disease but there is still suspicion of coronary artery disease. If this test detects disease that would have otherwise been undetected, a more proactive approach to address root causes will be encouraged. Beware of the slippery slope to a stress test, stents or surgery. Coronary Calcium Score is a “loss leader”for interventional cardiology programs. Call us first before scheduling further tests.
Home Sleep Testing and Auto Titrated CPAP: These tests have made diagnosis and management of sleep apnea more affordable and effective. Sleep apnea is a root cause of heart attack, stroke, atrial fibrillation, hypertension and heart failure. Treating it can lower your risk of these events, lower your blood pressure, and reduce arterial inflammation.
Oral Microbiome Testing: Oral microbiome testing involves taking a sample of saliva, and analyzing it in a laboratory to identify the types of bacteria present. If high risk bacteria species are found, they can contribute to arterial inflammation. In some cases, this can affect management of periodontal disease, which contributes to heart attack and stroke risk.
Knowing the nature of your oral “neighborhood” can prompt a more proactive approach to your oral hygiene. If there are dangerous criminals in your neighborhood, you will be more careful to “lock your doors” and augment your security for protection. The chronic diseases affected by your oral microbiome include periodontal disease, cardiovascular disease, Type 2 Diabetes and prediabetes, and even some cancers and dementia.
Is genetic testing worth the effort?
Genetic testing should be chosen with an emphasis on tests for which there is a treatment decision that can change the gene expression. Gene expression is the process by which our genes create proteins that perform different functions in our body, such as building and repairing tissues or fighting off infections…
Recommended genetic testing should emphasize tests for which there are meaningful remedies that can change the gene expression. Gene expression is the process by which our genes create proteins that perform different functions in our body, such as building and repairing tissues or fighting off infections.
Genetic testing in low-risk individuals with no plan for lifestyle or treatment changes is expensive, confusing and futile.
What genetic tests are most helpful?
Haptoglobin genotype is very worthwhile, especially those with Type 2 Diabetes, insulin resistance, or prediabetes. Most of us fall into one of these categories!
The cost of this test has decreased significantly over the years. In 2018 the test cost about $400. Now, the cost is $99, a small price for precision in personalized treatment. Because it isn’t offered by Quest or Cleveland Heart Lab, we use Boston Heart Diagnostics and provide you their kit to obtain the proper specimen as close to your home as possible at an affordable cost of $99 out of pocket. It is not covered by insurance, which might tell you the information can actually improve your health and reduce your costs!
How does haptoglobin genotype guide treatment?
The table below outlines the implications of knowing your haptoglobin genotype.
Haptoglobin Genotype Results and Recommendations
Haptoglobin (Hp) 1-1 is the genotype at the lowest risk for vascular events such as heart attack or stroke. Haptoglobin 1-2 doubles this risk (increases it by 200%). Both of these findings indicate that events are more likely to happen if an individual takes daily vitamin E supplements beyond what is contained in a multivitamin or diet.
Individuals with risk of macular degeneration may be taking supplements containing higher amounts of vitamin E. If your specialist is treating you for current macular degeneration, these supplements make sense. However, you should know that there is a tradeoff. Treating the risk of one condition may increase your risk of another. (See the table above for more information.)
Haptoglobin 2-2 genotype increases risk of vascular events by 500% (or 5x the baseline risk). Gluten should be avoided if this genotype is found, as it provokes a significant increase in inflammation, leading to a higher risk of events.
Individuals with the Haptoglobin 2-2 genotype should take a daily dose of 400 IU of Vitamin E mixed tocopherols to significantly reduce cardiovascular risk by 80%! The proof is greatest in those with Type 2 Diabetes, but most of us have the prediabetic curse that was a blessing when we ate like hunter gatherers.
What is the relevance of ApoE genotype?
We don’t order ApoE routinely, but if you want it, we can order it. In select situations, it can help guide dietary choices, but are less relevant if insulin resistance and carbohydrate restriction is the more compelling opportunity. It often adds more “noise” than “signal.”
The Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype is a genetic factor that plays a significant role in various aspects of human health, particularly in relation to lipid metabolism and the risk of developing certain diseases. The ApoE gene encodes a protein that is involved in the transport and metabolism of lipids, including cholesterol, in the body. There are three common variants or alleles of the ApoE gene: ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4.
The relevance of ApoE genotype lies in its association with several health conditions, including:
Alzheimer's Dementia: The ApoE4 allele is the strongest known genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). Individuals who inherit one copy of the ApoE4 allele from either parent have an increased risk of developing AD, while those who inherit two copies have an even higher risk. But if you are really interested in reducing your risk of dementia, read “Healthy Heart Healthy Brain” by Bale and Doneen and “The End of Alzheimers” by Dale Bredesen.
Cardiovascular Disease: The ApoE genotype is also linked to the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease and stroke. ApoE4 carriers have been found to have higher levels of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as "bad" cholesterol) and an increased susceptibility to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Lipid metabolism: The ApoE genotype influences how the body metabolizes lipids. ApoE2 is associated with lower levels of cholesterol and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, while ApoE4 is associated with higher cholesterol levels and an increased risk.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI): Research suggests that the ApoE4 allele may be associated with an increased risk of poorer outcomes following TBI, including a higher likelihood of developing neurodegenerative disorders later in life.
It's important to note that while the ApoE genotype can provide insights into an individual's predisposition to certain conditions, it does not determine with certainty whether someone will develop these diseases. Other genetic and environmental factors generally play a more compelling modifiable role, and individual health outcomes are complex and multifactorial. Genetic testing and counseling can help individuals understand their ApoE genotype and its implications, but it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and interpretation of genetic information.
What is the relevance of KIF6 genotype?
We rarely order the KIF6 genotype. Our preference for rosuvastatin makes it largely irrelevant to guide treatment. If you insist on using atorvastatin, pravastatin or simvastatin, I suggest verifying this is wise based on KIF6 predicting benefit.
The KIF6 (kinesin-like protein 6) genotype refers to a specific genetic variation in the KIF6 gene. This gene has been studied in relation to cardiovascular health and response to certain medications. However, it is important to note that the current understanding of the relevance of KIF6 genotype is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand its implications.
The KIF6 gene variant in question is known as KIF6 719Arg. It has been associated with an increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart attacks in some studies. Individuals who carry this genetic variant may have a higher likelihood of developing these cardiovascular conditions compared to those without the variant.
The KIF6 gene has also been investigated in the context of statin medications, which are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Some studies have suggested that individuals with the KIF6 719Arg variant may experience a greater reduction in cardiovascular events when treated with statins compared to those without the variant. However, these findings have not been consistently replicated across all studies.
There is evidence that those with the KIF6 719Arg variant get more benefit from atorvastatin and pravastatin than those not carrying that variant. We prefer rosuvastatin as effective despite genetic variation and less prone to exacerbate insulin resistance/diabetes or cross the blood/brain barrier affecting cognition. Most of our patients take 5 mg 3 days weekly or less with benefit documented with blood and ultrasound inflammation measures.
It's important to understand that genetic factors, including the KIF6 genotype, are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to cardiovascular health. Other factors such as lifestyle choices (e.g., diet, exercise), family history, and other genetic variations collectively contribute to an individual's risk for developing cardiovascular conditions.
Overall, while the KIF6 genotype has shown some associations with cardiovascular health and response to statin therapy, its clinical utility is still being explored, and further research is needed to determine its exact relevance and potential implications in healthcare practice.
For more information about genetic testing see our post about genes and how they affect your risk of heart attack.
What is a Coronary Artery Calcium Score?
A coronary artery calcium scan, which determines your coronary artery calcium score, is useful as a screening tool for those who are not known to have arterial disease…
A coronary artery calcium scan reports your coronary artery calcium score. It is useful as a screening tool for those who are not known to have arterial disease. It should not be used to assess symptoms or monitor arterial disease in response to therapy.
If you already know of the presence of arterial disease in your body (if you’ve had a stroke, heart attack, stent, or bypass surgery) or carotid artery ultrasound, determining this score is unnecessary. It may also lead to risky, costly/profitable stents or surgery with no benefit in the absence of symptoms like angina or heart failure.
What does the score mean?
A score of zero is generally reassuring that the risk of heart attack from silent arterial disease is low in studied populations. You want this score to be as low as possible. However, if you have other risk or evidence of arterial disease, you could have plaque that is not calcified, known as soft/homogeneous/vulnerable/or unstable plaque. This occurs in about 10% of those with zero calcium scores.
Non-calcified plaque is the most vulnerable to rupture (the event that leads to heart attack). Therefore, a score of zero does not guarantee that you will not have a heart attack. Plaque can still form after a reassuring test in response to a change in conditions that promote inflammation, such as a dental infection.
Coronary calcium scores rise as plaque heals and inflammation subsides. In our experience, scores rarely fall, which makes this scan inappropriate for measuring progress.
Instead, we recommend measuring trends of the thickness (sickness or inflammation) of your carotid arterial wall, which can be done with completely safe ultrasound. This is a much more meaningful measure of disease response to treatment. To find this option, click www.vasolabs.com/events.
Coronary artery calcium scans can lead to a slippery slope that can be dangerous to your health and your pocketbook. They can lead to unnecessary procedures, such as stents, that do not prevent heart attack or stroke in individuals with no symptoms.
If there is no plaque seen on carotid ultrasound, an elevated Coronary Artery Calcium Score should provoke a search for root causes and efforts to eliminate them.
The proper response to a positive screening/asymptomatic coronary artery calcium score should be to identify the root causes of arterial disease and eliminate them. This is what we do at the CureCenter.
If you have no history of heart attack, stroke, TIA, stent, bypass or other evidence of arterial disease, we suggest first getting a carotid ultrasound to screen for plaque as the first step. You can do this by scheduling your 15-minute CureScreen.
If you’re unsure what to do next, request a no cost/no obligation Discovery Zoom Call today.
Get Started on the Path to a Long and Healthy Life
Participate in a 15-30 minute Zoom or phone call with Dr. Backs. Your questions about process, cost, insurance coverage and expectations will be answered. You will decide together if the CureCenter and a CurePlan are right for you.
Located in Central Illinois? Schedule your 15-minute CureScreen for arterial disease. It’s quick, painless, and is the first step toward preventing the most common cause of death and disability.